

Levene did a lot of research and published many papers on the science of molecular biology. Phoebus Levene conducted intensive investigations of the structure of the nuclein as it was known then.

Further study on the structure of the DNA model A lot of texts on the history of science in the nineteenth century failed to mention him completely. Miescher, unfortunately, received very little recognition for his discovery. This substance had an unusually high amount of phosphorus and was resistant to protein digestion. During his experiments, he discovered a substance that was different from any other protein. He was trying to identify the proteins that make up the white blood cells. Interestingly, Miescher wasn’t trying to discover DNA. Shortened to DNA, the abbreviation is most widely known today. This later became known as nucleic acid and then, later on, deoxyribonucleic acid as more was learned about the molecule. The chemist, Frederich Miescher, discovered DNA, although he first called it a nuclein. The work done by these earlier scientists formed the foundation for the discovery of the double helix structure of the DNA molecule by Watson and Crick. Rosalind Franklin’s work provided the foundation for the DNA model. However, she passed away before the 1962 prize and Nobel prizes are not awarded posthumously. In truth, it is much of Rosalind Franklin’s work that led to the discovery of the DNA model. Ultimately, Maurice Wilkins shared the 1962 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine with James Watson and Francis Crick but is not given as much of the credit.
#SUGAR PHOSPHATE BACKBONE IN DNA CRACK#
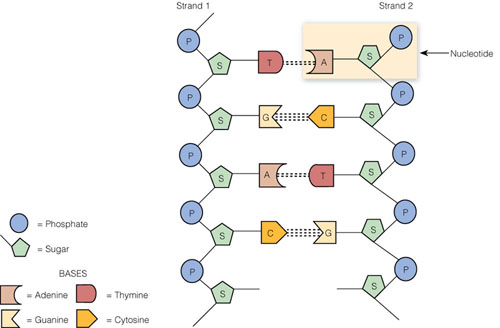
Then, Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins produced the x-ray crystallography photographs ultimately used by Watson and Crick to crack the genetic code. Later research by Russian scientist Phoebus Levene and Austrian Erwin Chargaff served to unearth more information about the DNA molecule. However, the first identification of DNA was actually made in 1869 by Frederich Miescher, a Swiss scientist. Scientists James Watson and Francis Crick are often credited to have discovered the DNA model in the 1950s. CC- CC0 1.0 Universal Public Domain Dedication. You can get a feel for how the two strands are woven together by twisting two pipe cleaners. The sides are commonly known as the sugar phosphate backbone. The rungs on the ladder are the nitrogenous base pairs connected by a hydrogen bond (bases adenine and thymine or guanine and cytosine) while the sides are alternating sugar molecules and phosphate groups bonded together. The Structure of the DNA ModelĮach DNA single strand comprises three parts:ĭNA molecules have two strands that coil around an axis, forming a twisted ladder shape, commonly known as a double helix. This article takes us through the structure of a DNA molecule and the history behind the discovery of this structure. Their work was based on the x-ray crystallography structures collected and analyzed by another scientist, Rosalind Franklin. The first accurate DNA double helix structure model was unveiled in 1962 and credited to two scientists, James Watson and Francis Crick. Moscow International Business Center, Evolution Tower. Designers and engineers from all around the world have even been inspired by the shape to design various structures, including the Evolution Tower in Moscow Russia and various statues and stairways. The double-helical shape reminiscent of a twisting ladder can be recognized by many people outside of the scientific professions. The structure of a DNA model is an interesting one.
Further study on the structure of the DNA model.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
